Published on Jun 05, 2023
Air Powered Cars
Have you been to the gas station this week? Considering that we live in a very mobile society, it's probably safe to assume that you have. While pumping gas, you've undoubtedly noticed how much the price of gas has soared in recent years. Gasoline which has been the main source of fuel for the history of cars, is becoming more and more expensive and impractical (especially from an environmental standpoint). These factors are leading car manufacturers to develop cars fueled by alternative energies. Two hybrid cars took to the road in 2000, and in future years fuel-cell-powered cars will roll onto the world's highways.
While gasoline prices in the United States have not yet reached their highest point ($2.66/gallon in 1980), they have climbed steeply in the past years. In 1999, prices rose by 30 percent, and from December 1999 to October 2000, prices rose an additional 20 percent, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. In Europe, prices are even higher, costing more than $4 in countries like England and the Netherlands. But cost is not the only problem with using gasoline as our primary fuel. It is also damaging to the environment, and since it is not a renewable resource, it will eventually run out. One possible alternative is the air-powered car.
Air Powered Cars runs on compressed air instead of gasoline. This car is powered by a two cylinder compressed engine. This engine can run either on compressed air alone or act as an IC engine. Compressed air is stored in glass or fiber tanks at a pressure of 4351 psi.
Vehicle Parts
Compressed air tanks
One of the most frequently asked questions is about the safety of the compressed air storage tanks. These tanks hold 90 cubic meters of air compressed to 300 bars. Many people ask whether this system is dangerous in case of an accident and if there is a risk of explosion. The answer is NO. Why? Because these are the same tanks used to carry the liquid gas used by buses for public transport. The tanks enjoy the same technology developed to contain natural gas. They are designed and officially approved to carry an explosive product: methane gas.
In the case of a major accident, where the tanks are ruptured, they would not explode since they are not metal. Instead they would crack, as they are made of carbon fiber. An elongated crack would appear in the tank, without exploding, and the air would simply escape, producing a loud but harmless noise. Of course, since this technology is licensed to transport an inflammable and explosive gas (Natural gas), it is perfectly capable inoffensive and non-flammable air.
The Air Filter
The MDI engine works with both air taken from the atmosphere and air pre-compressed in tanks. Air is compressed by the on-board compressor or at service stations equipped with a high-pressure compressor.
Before compression, the air must be filtered to get rid of any impurities that could damage the engine. Carbon filters are used to eliminate dirt, dust, humidity and other particles, which unfortunately, are found in the air in our cities.
This represents a true revolution in automobiles - it is the first time that a car has produced minus pollution, i.e. it eliminates and reduces existing pollution rather than emitting dirt and harmful gases. The exhaust pipe on the MDI cars produces clean air, which is cold on exit (between -15º and 0º) and is harmless to human life. With this system the air that comes out of the car is cleaner than the air that went in.
Technology Description
The following is the technology description of the actual functionality of the motor. A more detailed explanation can be found in U.S. patent no: 6,334,435 .
Process Description
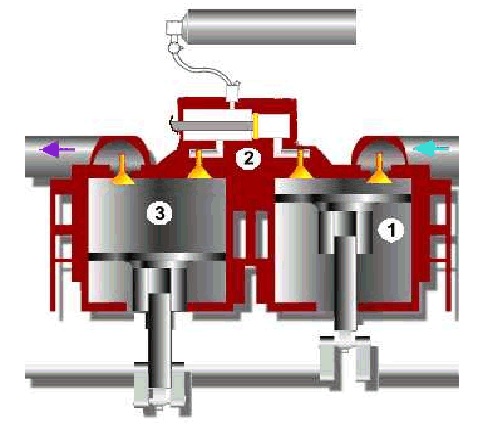
1. The first piston takes in ambient air and compresses it to approximately 300 psi and 200*f in the compression chamber during the first cycle of the engine.
2. When the piston pause, a small amount of compressed air from the tanks is released into the expansion chamber to create a low pressured, low temperature volume of about 140psi
3. Shortly before the valve to the exhaust cylinder is opened, a high-speed shutter connects the compression and expansion chambers. The sudden pressure and temperature difference between the low chambers creates pressure waves in the expansion chamber, thereby producing work in the exhaust chamber that drives the piston to power the engine.
The air tanks for storing the compressed air are localized underneath the vehicle. They are constructed of reinforced carbon fiber with a thermoplastic liner. Each tank can hold 3,180 ft3 of air at a pressure of up to 4,300 psi. When connected to a special compressor station, the tanks can be recharged within 3-4 minutes. They can also be recharged using the on-board compressor 3-4 hours after connecting to a standard power outlet.
How does the air tanks work and are there any issues with their safety?
One of the most frequently asked questions regards the safety of the air tanks, which store 90m3 of air at 300 bars of pressure. Many people ask whether this system is dangerous in case of an accident, and whether there is an explosion risk involved. The answer is NO. Why? Because the tanks are the ones already used to carry liquefied gases on some urban buses, and therefore make use of the technology that is already used to move buses on natural gas. That means that the tanks are prepared and certified to carry an explosive product: methane gas.
In the case of an accident, with air tank breakage, there would be no explosion or shattering, now that the tanks are not metallic. Due to the fact that they are made of glass fibre the tanks would crack longitudinally, and the air would escape, causing a strong buzzing sound with no dangerous factor. It is clear that if this technology has been tested and prepared to carry an inflammable and explosive gas, it can also be used to carry air.
A final matter with reference to the air tanks is the improvement that MDI contributed to the original structure. In order to avoid the so-called 'rocket effect', this means to avoid the air escaping through one of the tank's extremities causing a pressure leak that could move the car, MDI made a small but important change in the design. The valve on the buses' tanks are placed on one of the extremities. MDI has placed the valve in the middle of the tank reducing the 'rocket effect' to a minimum.